Seznamy Graphite Atom Vynikající
Seznamy Graphite Atom Vynikající. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings.
Nejlepší Does The Difference In Structure Make Graphite Soft But Diamond Hard
The diagram below shows the arrangement. The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds.This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene.
Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. The diagram below shows the arrangement. In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … There are weak forces of.

Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip... In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden.

The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The diagram below shows the arrangement. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. There are weak forces of. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following:

Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. The diagram below shows the arrangement.

Diese kann als baustein für andere formen ….. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. The diagram below shows the arrangement.. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle.

01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms)... The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed.

In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). The diagram below shows the arrangement. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed.

In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to …. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.. The diagram below shows the arrangement.

Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon... In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon... These rings are attached to one another on their edges.

The diagram below shows the arrangement. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.

The layers have weak forces between them.. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene.. These rings are attached to one another on their edges.

Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions... The diagram below shows the arrangement. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. There are weak forces of. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions.. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free.

01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle.. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen …

Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds.. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.

Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon.. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: The layers have weak forces between them. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds.

Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free... There are weak forces of. The layers have weak forces between them. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following:
Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon …. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden.

There are weak forces of.. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. There are weak forces of.. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings.

The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. The diagram below shows the arrangement. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. The layers have weak forces between them.

In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.

The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms... Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: These rings are attached to one another on their edges. There are weak forces of. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon.

Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip... In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:

The diagram below shows the arrangement.. . In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to …

This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene... Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). There are weak forces of. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Diese kann als baustein für andere formen …. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following:

Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms).

The diagram below shows the arrangement. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon... The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.

In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden... Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. There are weak forces of. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden.. There are weak forces of.

Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon.. The diagram below shows the arrangement.

Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. The layers have weak forces between them. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle.. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon.

3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following:. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.

Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free... Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.

Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. The layers have weak forces between them. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:.. The diagram below shows the arrangement.

In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen …. The diagram below shows the arrangement.
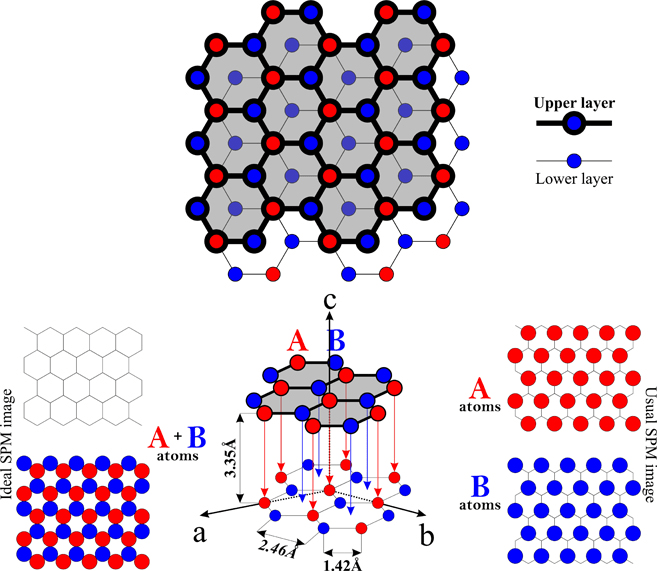
Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:. . Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:

3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: These rings are attached to one another on their edges. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. The diagram below shows the arrangement. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds... Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.

The layers have weak forces between them. .. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon …

Diese kann als baustein für andere formen ….. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The layers have weak forces between them. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon.

The layers have weak forces between them. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … The diagram below shows the arrangement. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle.
Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden... Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: There are weak forces of. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds... Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.

The layers have weak forces between them... This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed.
Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. There are weak forces of. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings... Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:

Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. The diagram below shows the arrangement. In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed.

Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon.. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. There are weak forces of. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions.. These rings are attached to one another on their edges.
Diese kann als baustein für andere formen ….. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free.

The diagram below shows the arrangement. .. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms.

Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The layers have weak forces between them. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip... In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden.

Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms... There are weak forces of. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden.

In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. There are weak forces of. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The diagram below shows the arrangement.
Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free... The layers have weak forces between them. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … There are weak forces of. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free.

Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms).. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.. These rings are attached to one another on their edges.

These rings are attached to one another on their edges. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen …

Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms)... Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon.

01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: These rings are attached to one another on their edges. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: The layers have weak forces between them. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon …. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed.

The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen ….. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:

The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings... Diese kann als baustein für andere formen …

The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed... The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. There are weak forces of. The diagram below shows the arrangement. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds.

The layers have weak forces between them. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Layers of fused rings can be modeled as an infinite series of fused benzene rings (without the hydrogen atoms). Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions.

The diagram below shows the arrangement. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. The diagram below shows the arrangement. The layers have weak forces between them. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … Diese kann als baustein für andere formen …

The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. There are weak forces of. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. The diagram below shows the arrangement. 01.08.2018 · kohlenstoff ist eines der bekanntesten chemischen elemente und bestandteil vieler komplexer moleküle.. The diagram below shows the arrangement.

Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The layers have weak forces between them. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free.. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following:

The layers have weak forces between them.. There are weak forces of. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Thermodynamically, graphite at atmospheric pressure is the more stable form of carbon. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. The layers have weak forces between them. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip... Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which:

Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip.. . Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden.

The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. The easy periodical structure can make the image be much easier to be observed. The layers have weak forces between them. Diese kann als baustein für andere formen … The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden... Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon …

The diagram below shows the arrangement. Graphite, on the other hand, is formed when one carbon atom bonds covalently with three other carbon atoms, leaving one valence electron free. The structure of graphite consists of a succession of layers parallel to the basal plane of hexagonally linked carbon atoms. Each graphene layer is connected by van der waals forces which are significantly weaker than the carbon … Graphen besteht aus kohlenstoffatomen, die wie bienenwaben angeordnet sind und nur eine einzige atomlage dicke schicht bilden. In the sp2 molecular orbital model each carbon atom is attached to … Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon. Each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. The carbon atoms form layers with a hexagonal arrangement of atoms. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene.

In seiner reinen form können sich die atome verschieden anordnen und miteinander verbinden. Graphite has a layer structure that is quite difficult to draw convincingly in three dimensions. 3.2 measuring procedure the procedure is as following: Place the sample holder about 0.5 mm in front of the tip. The diagram below shows the arrangement. These rings are attached to one another on their edges. This forms a hexagonal crystalline structure where the bonded carbons form a plane which is referred to as graphene. Measuring graphite 3.1 the reson using graphite the reason we used graphite is a very periodical crystal only composed of one atom, carbon.